
 Research Assistant at Nanyang Technological University (NTU)
Research Assistant at Nanyang Technological University (NTU) M.A. in Journalism and Communication, Wuhan University
M.A. in Journalism and Communication, Wuhan UniversityI am currently working as a remote Research Assistant at the Wee Kim Wee School of Communication and Information (WKWSCI), Nanyang Technological University (NTU), Singapore, My research focuses on AI trust and psychological communication, exploring how emerging technologies influence human behavior and trust in media at the intersection of communication, sociology, and psychology.
I hold both a Bachelor’s and a Master of Arts degree from the School of Journalism and Communication at Wuhan University. My professional experiences at China Media Group, Meituan, and Blue Focus Digital have provided practical skills in research and data analysis. I am seeking Ph.D. opportunities to advance research on AI-driven communication and its societal impact, and I welcome collaboration and discussion in this field.
Warning
Problem: The current name of your GitHub Pages repository ("Solution: Please consider renaming the repository to "
http://".
However, if the current repository name is intended, you can ignore this message by removing "{% include widgets/debug_repo_name.html %}" in index.html.
Action required
Problem: The current root path of this site is "baseurl ("_config.yml.
Solution: Please set the
baseurl in _config.yml to "Education
-
 Wuhan UniversitySchool of Journalism and Communication
Wuhan UniversitySchool of Journalism and Communication
M.A in Journalsim and CommunicationSep 2023 - Jul 2025 -
 Wuhan UniversitySchool of Journalism and Communication
Wuhan UniversitySchool of Journalism and Communication
B.A. in Radio and TelevisionSep 2019 - Jul 2023
Experience
-
 Nanyang Technological UniversityResearch Assistant
Nanyang Technological UniversityResearch Assistant
Wee Kim Wee School of Communication and Information (WKWSCI)Aug 2025 - Present -
 Tsinghua UniversityResearch Assistant
Tsinghua UniversityResearch Assistant
School of Journalism and CommunicationJul 2025 - Aug 2025 -
 China Central TelevisionIntern
China Central TelevisionIntern
Advertising Culture and Tourism Marketing DepartmentMar 2022 - Jul 2022 -
 MeituanIntern
MeituanIntern
User Product & Content OperationsMay 2022 - Jun 2022 -
 BlueFocusIntern
BlueFocusIntern
Public Relations & Marketing InternOct 2021 - Dec 2021
Honors & Awards
-
Outstanding Scholarship for Graduate Students, Wuhan UniversityDec 2024
-
Outstanding Graduate Students, Wuhan UniversityDec 2024
-
National Gold Award, the 16th China Chorus FestivalJan 2021
-
Second Prize in Hubei Province, 'Telling a Good Chinese Story' Creative Communication CompetitionJan 2021
-
Active Contributor to Social Activities, Wuhan UniversityMay 2020
-
First Runner-up, Freshman Debate Tournament, School of Journalism and CommunicationOct 2019
News
Selected Publications (view all )
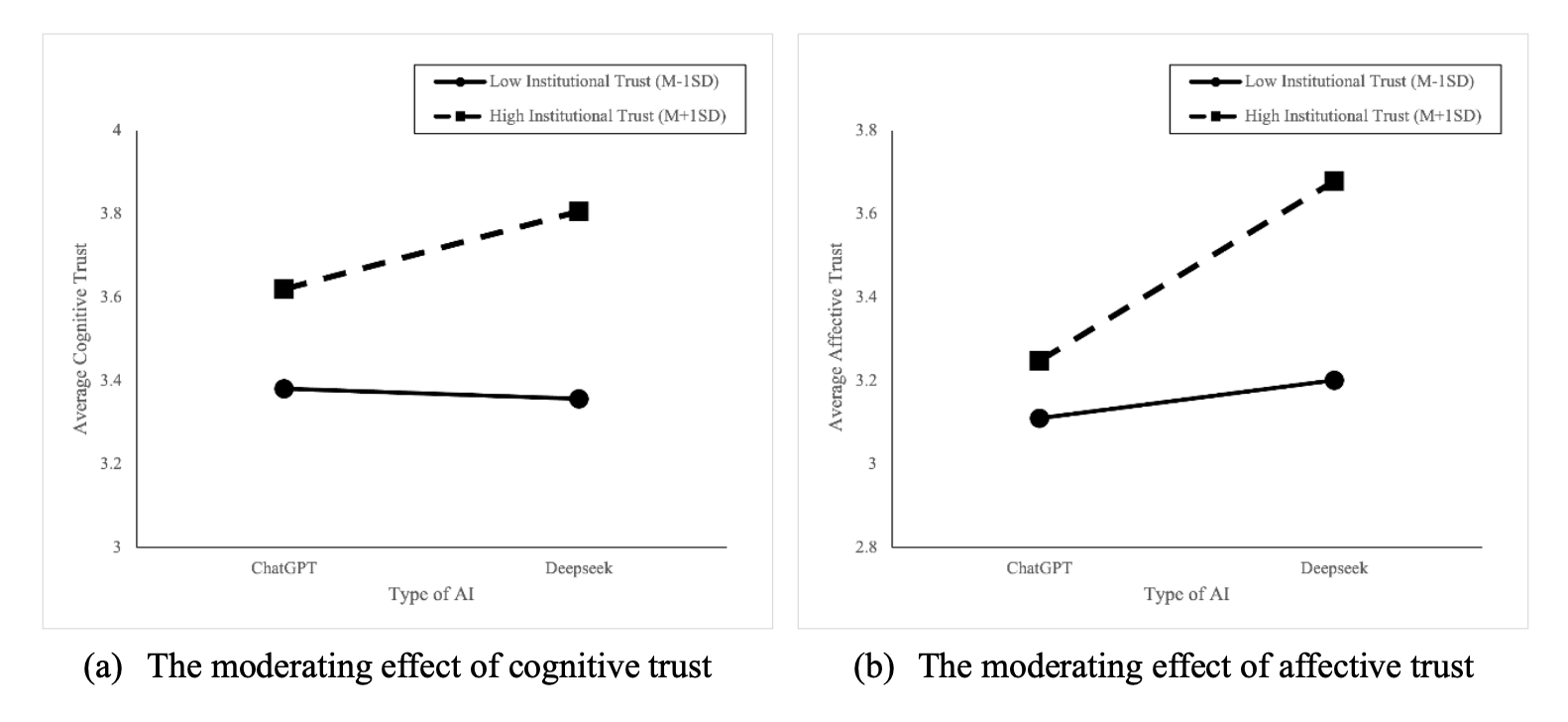
The Institutional Filter: How Trust Shapes Inequalities Between Domestic and Global AI Models
Conference of the International Association for Media and Communication Research (IAMCR) Under review. 2026
The Institutional Filter: How Trust Shapes Inequalities Between Domestic and Global AI Models
Conference of the International Association for Media and Communication Research (IAMCR) Under review. 2026
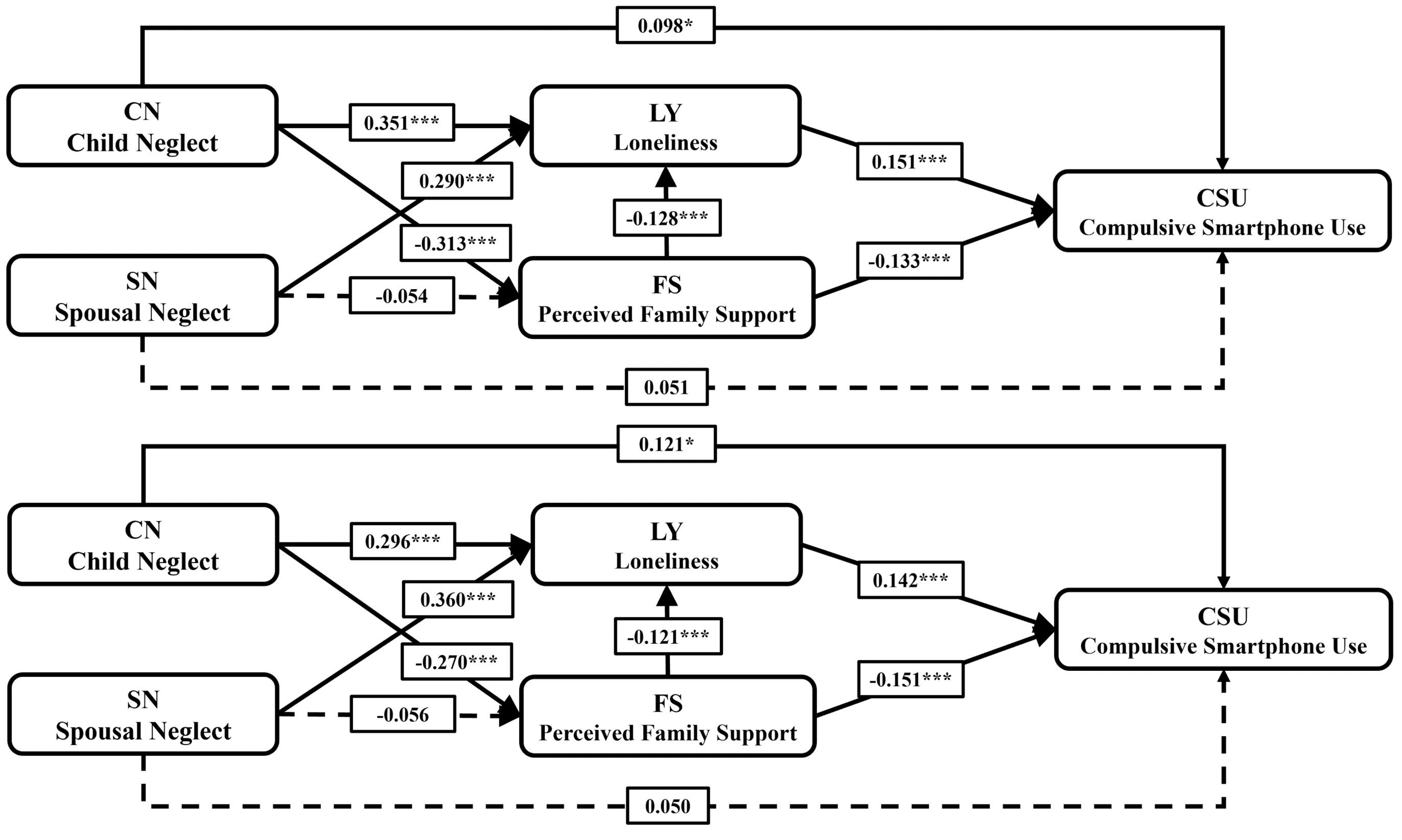
Aging Alone in a Connected World: The Impact of Family Neglect on Smartphone Dependence in Contemporary China
Yu Jia, Jiashen Huang, Wenjing Pan
Mobile Media & Communication (MMC) Under review. 2025
Aging Alone in a Connected World: The Impact of Family Neglect on Smartphone Dependence in Contemporary China
Yu Jia, Jiashen Huang, Wenjing Pan
Mobile Media & Communication (MMC) Under review. 2025
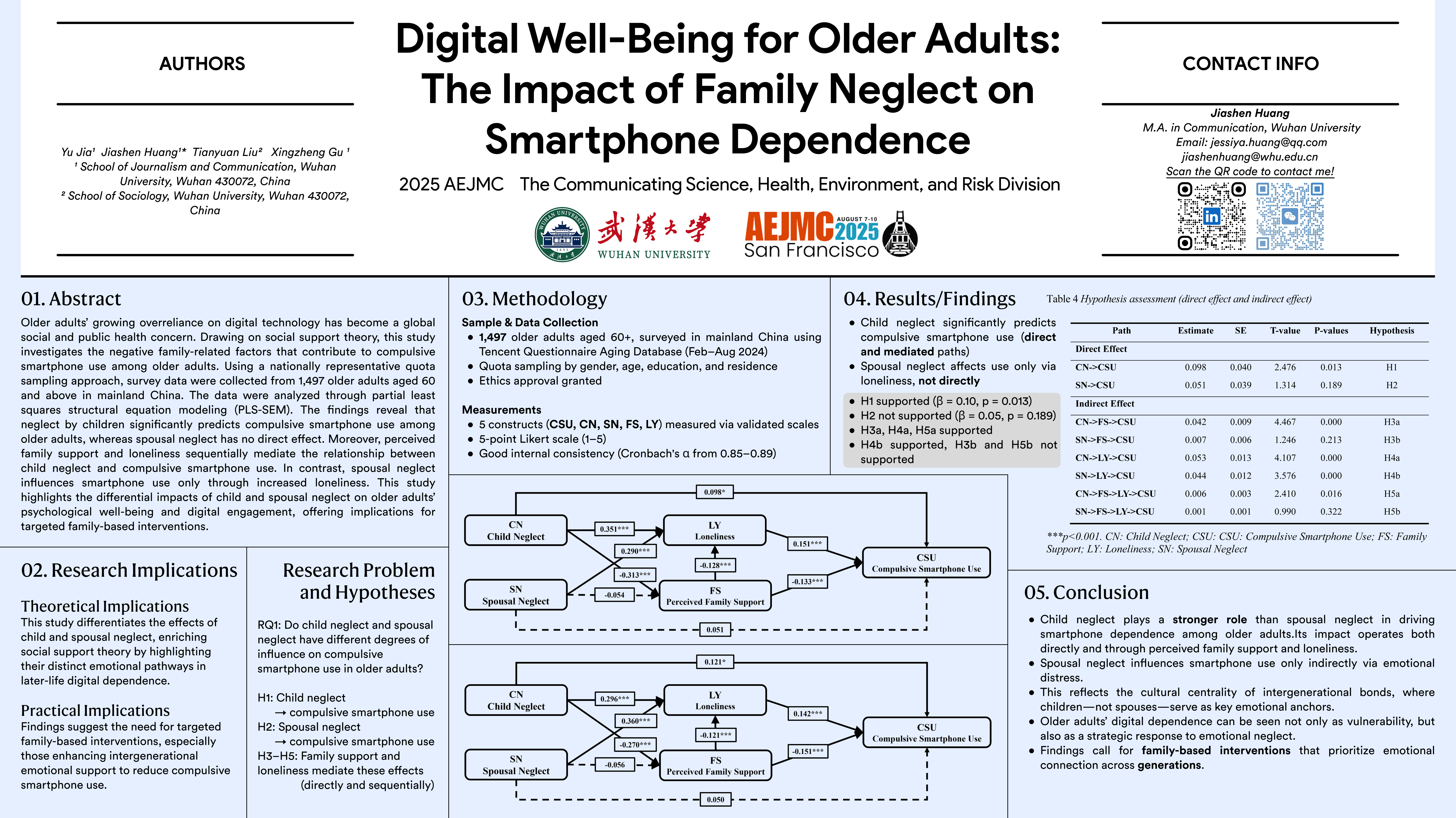
Digital Well-Being for Older Adults: The Impact of Family Neglect on Smartphone Dependence
Yu Jia, Jiashen Huang, Tianyuan Liu
2025 Association for Education in Journalism and Mass Communication Annual Conference (AEJMC) 2025
The excessive reliance and addiction of older adults to digital technology are increasingly evolving into a global social and public health challenge. Grounded in social support theory, this study investigates the negative family factors that contribute to compulsive smartphone use among older adults. Using a nationally representative quota sampling approach, we collected survey data from 1,497 older adults aged 60 and above in mainland China. The data were analyzed through partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM). The findings reveal that child neglect significantly fosters compulsive smartphone use among older adults, whereas partner neglect has no direct effect. Moreover, perceived family support and loneliness mediate the relationship between child neglect and compulsive smartphone use, with a sequential mediation effect observed between them. In contrast, partner neglect influences compulsive smartphone use only through increased loneliness. This study highlights the differential impacts of child neglect and partner neglect on older adults’ psychological well-being and digital consumption habits, providing theoretical and empirical support for developing targeted intervention strategies.
Digital Well-Being for Older Adults: The Impact of Family Neglect on Smartphone Dependence
Yu Jia, Jiashen Huang, Tianyuan Liu
2025 Association for Education in Journalism and Mass Communication Annual Conference (AEJMC) 2025
The excessive reliance and addiction of older adults to digital technology are increasingly evolving into a global social and public health challenge. Grounded in social support theory, this study investigates the negative family factors that contribute to compulsive smartphone use among older adults. Using a nationally representative quota sampling approach, we collected survey data from 1,497 older adults aged 60 and above in mainland China. The data were analyzed through partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM). The findings reveal that child neglect significantly fosters compulsive smartphone use among older adults, whereas partner neglect has no direct effect. Moreover, perceived family support and loneliness mediate the relationship between child neglect and compulsive smartphone use, with a sequential mediation effect observed between them. In contrast, partner neglect influences compulsive smartphone use only through increased loneliness. This study highlights the differential impacts of child neglect and partner neglect on older adults’ psychological well-being and digital consumption habits, providing theoretical and empirical support for developing targeted intervention strategies.
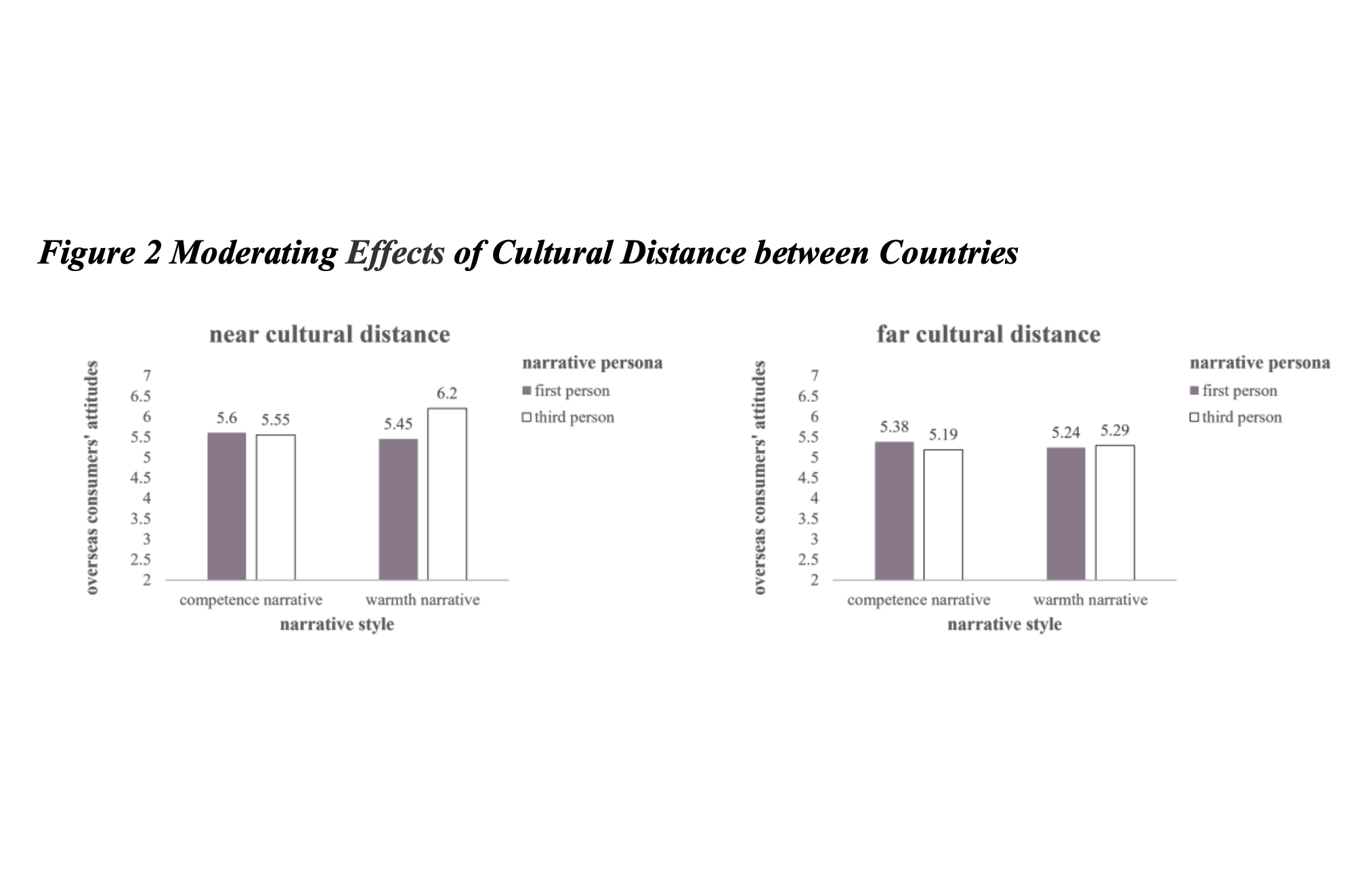
How do Brands Communicate with Overseas Audiences? The Matching Effect between Narrative Style and Narrative Person
Yu Jia, Jinyan Yu, Jiashen Huang, Ying You
2024 National Communication Association 110th Annual Convention (NCA) 2024
The international communication of brand has become an important issue in international trade. In this context, this paper chooses two important communication variables, brand narrative style and narrative person, to discuss the matching effect between brand narrative style (warmth vs. ability) and narrative person (first-person vs. third-person) and its impact on overseas audiences. In this paper, the main effect research based on big data crawling, laboratory experiment research on mediating effect and cross-cultural experimental research on regulating effect are carried out respectively. It is found that the interaction between brand narrative style and narrative person has a significant impact on consumer brand attitude. As for the warm brand narrative, compared with the third-person, the first-person narrative is helpful to improve consumers' brand attitude; For competency-based brand narrative, compared with the first-person, the third-person narrative is helpful to improve consumers' brand attitude. Information processing fluency has a mediating effect on the process. The interactive impact of brand narrative style and narrative person on overseas consumers' brand attitudes is moderated by the cultural distance between the home country and the host country. This matching effect is more significant for overseas consumers with close cultural distance, while it is less significant for overseas consumers with far cultural distance.
How do Brands Communicate with Overseas Audiences? The Matching Effect between Narrative Style and Narrative Person
Yu Jia, Jinyan Yu, Jiashen Huang, Ying You
2024 National Communication Association 110th Annual Convention (NCA) 2024
The international communication of brand has become an important issue in international trade. In this context, this paper chooses two important communication variables, brand narrative style and narrative person, to discuss the matching effect between brand narrative style (warmth vs. ability) and narrative person (first-person vs. third-person) and its impact on overseas audiences. In this paper, the main effect research based on big data crawling, laboratory experiment research on mediating effect and cross-cultural experimental research on regulating effect are carried out respectively. It is found that the interaction between brand narrative style and narrative person has a significant impact on consumer brand attitude. As for the warm brand narrative, compared with the third-person, the first-person narrative is helpful to improve consumers' brand attitude; For competency-based brand narrative, compared with the first-person, the third-person narrative is helpful to improve consumers' brand attitude. Information processing fluency has a mediating effect on the process. The interactive impact of brand narrative style and narrative person on overseas consumers' brand attitudes is moderated by the cultural distance between the home country and the host country. This matching effect is more significant for overseas consumers with close cultural distance, while it is less significant for overseas consumers with far cultural distance.
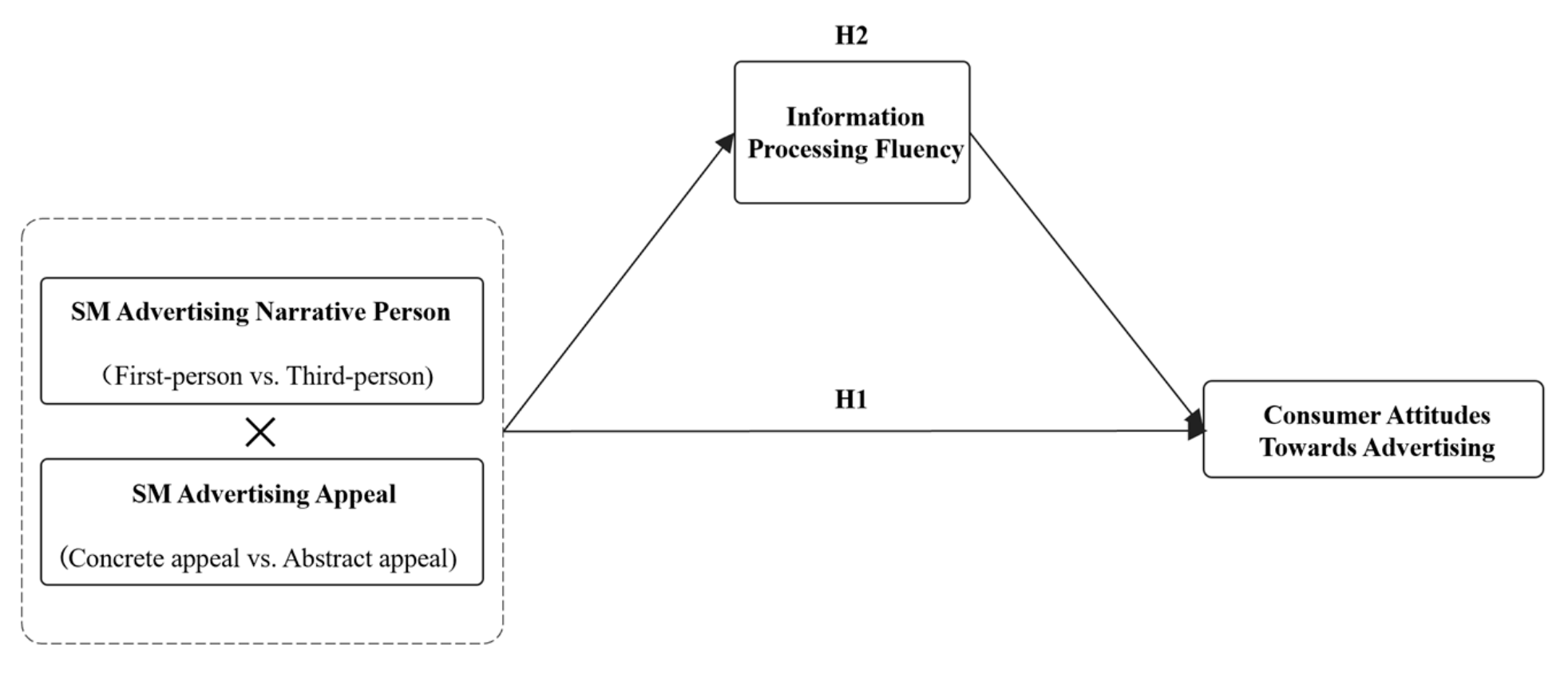
Research on the Matching Effect of Social Media Advertising Appeal and Narrative Person: Evidence from China
Yu Jia, Jinyan Yu, Tianyuan Liu, Jiashen Huang, Wenlong Mu, Fengfeng Deng
Journal of Theoretical and Applied Electronic Commerce Research (JTAER) 2024
The burgeoning landscape of social media advertising also faces a myriad of challenges. This study aims to explore the interactive effect of advertising appeal (abstract vs. concrete) and narrative person (first-person vs. third-person) on consumer attitudes towards social media advertising. Based on the construal level theory, this study uses secondary data and two experiments to investigate the interactive effect between advertising appeal and narrative person in social media advertising and the moderated mediating role of information processing fluency. The result reveals that a harmonious match between advertising appeal and narrative person enhances consumer fluency in processing advertising information, thereby improving consumer attitudes towards advertising. Specifically, for advertisements with concrete appeal, first-person narratives are more conducive to enhancing consumer attitudes towards advertising. Conversely, for advertisements with abstract appeal, third-person narratives are more advantageous. This study provides theoretical insights into social media advertising narration, with practical implications for marketers to advance social media advertising design.
Research on the Matching Effect of Social Media Advertising Appeal and Narrative Person: Evidence from China
Yu Jia, Jinyan Yu, Tianyuan Liu, Jiashen Huang, Wenlong Mu, Fengfeng Deng
Journal of Theoretical and Applied Electronic Commerce Research (JTAER) 2024
The burgeoning landscape of social media advertising also faces a myriad of challenges. This study aims to explore the interactive effect of advertising appeal (abstract vs. concrete) and narrative person (first-person vs. third-person) on consumer attitudes towards social media advertising. Based on the construal level theory, this study uses secondary data and two experiments to investigate the interactive effect between advertising appeal and narrative person in social media advertising and the moderated mediating role of information processing fluency. The result reveals that a harmonious match between advertising appeal and narrative person enhances consumer fluency in processing advertising information, thereby improving consumer attitudes towards advertising. Specifically, for advertisements with concrete appeal, first-person narratives are more conducive to enhancing consumer attitudes towards advertising. Conversely, for advertisements with abstract appeal, third-person narratives are more advantageous. This study provides theoretical insights into social media advertising narration, with practical implications for marketers to advance social media advertising design.
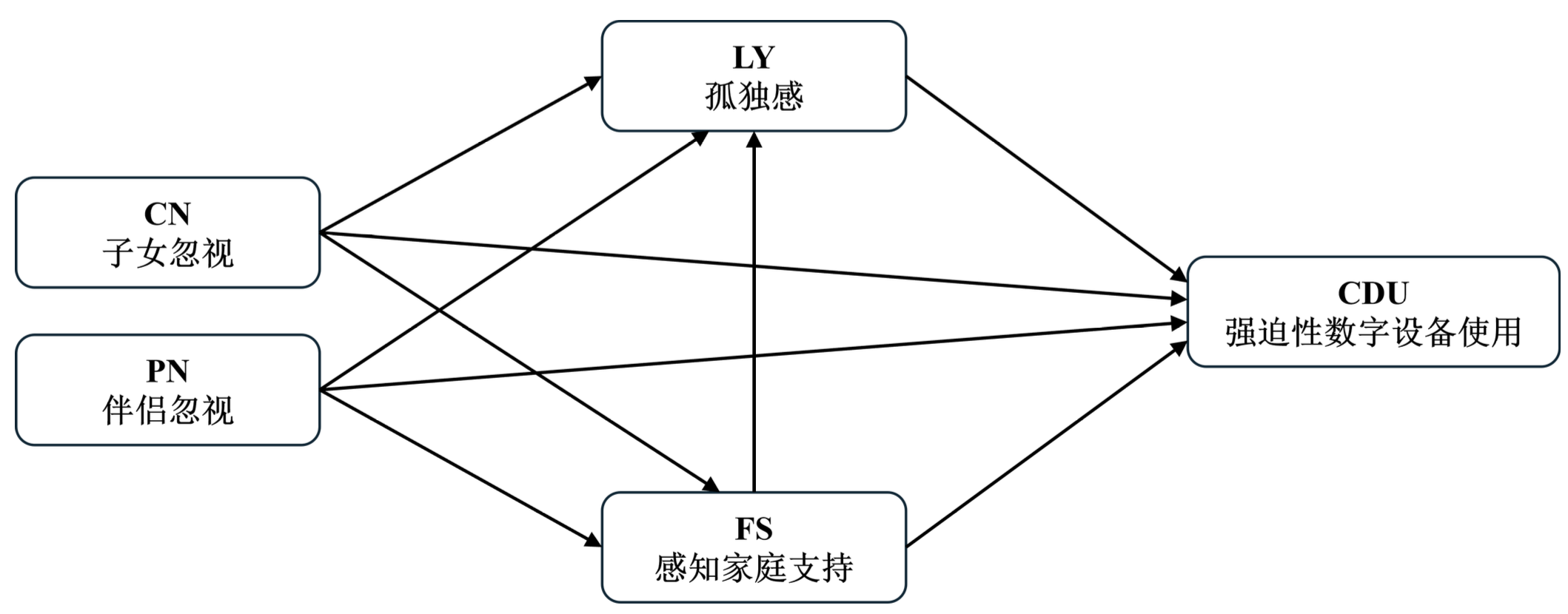
数字时代的孤独:伴侣与子女忽视如何影响老年人数字设备沉迷?
Loneliness in the Digital Age: How Partner and Child Neglect Affects Digital Device Addiction in Older Adults?
Yu Jia, Jiashen Huang, Xingzheng Gu, Tianyuan Liu
2024年中国新闻史学会健康传播委员会年会
2024 Annual Meeting of the Health Communication Professional Committee of the Chinese Society for the History of Journalism 2024
The excessive reliance on and addiction to digital technology among older adults is gradually evolving into a global social and public health challenge. Based on social support theory, this study delves into the family factors inducing compulsive digital device use among older adults. Through national quota sampling, survey data from 1497 older adults aged 60 and above in mainland China were ultimately collected, and the questionnaire data were analyzed using partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM). The research results indicate that children's neglect of older adults significantly promotes compulsive digital device use among older adults, while spousal neglect has no direct impact on this behavior. Furthermore, family support and loneliness play independent mediating and sequential mediating roles between children's neglect and compulsive digital device use among older adults. Spousal neglect can only affect compulsive digital device use among older adults by increasing their loneliness. This study reveals the different impacts of children's neglect and spousal neglect on the mental health and digital usage habits of older adults, providing theoretical support and empirical evidence for developing stratified and categorized intervention measures.
数字时代的孤独:伴侣与子女忽视如何影响老年人数字设备沉迷?
Loneliness in the Digital Age: How Partner and Child Neglect Affects Digital Device Addiction in Older Adults?
Yu Jia, Jiashen Huang, Xingzheng Gu, Tianyuan Liu
2024年中国新闻史学会健康传播委员会年会
2024 Annual Meeting of the Health Communication Professional Committee of the Chinese Society for the History of Journalism 2024
The excessive reliance on and addiction to digital technology among older adults is gradually evolving into a global social and public health challenge. Based on social support theory, this study delves into the family factors inducing compulsive digital device use among older adults. Through national quota sampling, survey data from 1497 older adults aged 60 and above in mainland China were ultimately collected, and the questionnaire data were analyzed using partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM). The research results indicate that children's neglect of older adults significantly promotes compulsive digital device use among older adults, while spousal neglect has no direct impact on this behavior. Furthermore, family support and loneliness play independent mediating and sequential mediating roles between children's neglect and compulsive digital device use among older adults. Spousal neglect can only affect compulsive digital device use among older adults by increasing their loneliness. This study reveals the different impacts of children's neglect and spousal neglect on the mental health and digital usage habits of older adults, providing theoretical support and empirical evidence for developing stratified and categorized intervention measures.
Abstract or Concrete? Research on the Matching Effect of Social Media Advertising Appeals and Narrative Person
Yu Jia, Jinyan Yu, Jiashen Huang, Tianyuan Liu, Wenlong Mu
2024年互动营销国际研讨会
2024 International Symposium and Workshop of Interactive Marketing 2024
The excessive reliance on and addiction to digital technology among older adults is gradually evolving into a global social and public health challenge. Based on social support theory, this study delves into the family factors inducing compulsive digital device use among older adults. Through national quota sampling, survey data from 1497 older adults aged 60 and above in mainland China were ultimately collected, and the questionnaire data were analyzed using partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM). The research results indicate that children's neglect of older adults significantly promotes compulsive digital device use among older adults, while spousal neglect has no direct impact on this behavior. Furthermore, family support and loneliness play independent mediating and sequential mediating roles between children's neglect and compulsive digital device use among older adults. Spousal neglect can only affect compulsive digital device use among older adults by increasing their loneliness. This study reveals the different impacts of children's neglect and spousal neglect on the mental health and digital usage habits of older adults, providing theoretical support and empirical evidence for developing stratified and categorized intervention measures.
Abstract or Concrete? Research on the Matching Effect of Social Media Advertising Appeals and Narrative Person
Yu Jia, Jinyan Yu, Jiashen Huang, Tianyuan Liu, Wenlong Mu
2024年互动营销国际研讨会
2024 International Symposium and Workshop of Interactive Marketing 2024
The excessive reliance on and addiction to digital technology among older adults is gradually evolving into a global social and public health challenge. Based on social support theory, this study delves into the family factors inducing compulsive digital device use among older adults. Through national quota sampling, survey data from 1497 older adults aged 60 and above in mainland China were ultimately collected, and the questionnaire data were analyzed using partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM). The research results indicate that children's neglect of older adults significantly promotes compulsive digital device use among older adults, while spousal neglect has no direct impact on this behavior. Furthermore, family support and loneliness play independent mediating and sequential mediating roles between children's neglect and compulsive digital device use among older adults. Spousal neglect can only affect compulsive digital device use among older adults by increasing their loneliness. This study reveals the different impacts of children's neglect and spousal neglect on the mental health and digital usage habits of older adults, providing theoretical support and empirical evidence for developing stratified and categorized intervention measures.